What is PCBA and Why It Matters in Electronics
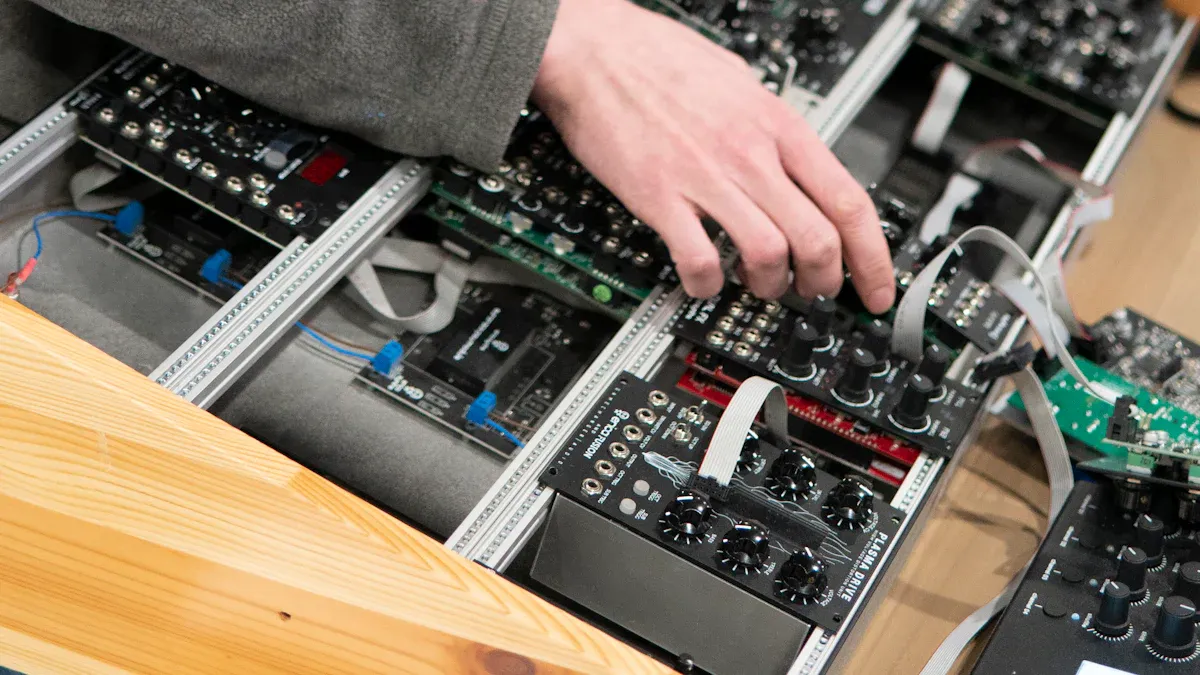

PCBA stands for Printed Circuit Board Assembly. According to industry standards, PCBA is the finished board created after all electronic components have been soldered and installed onto a printed circuit board. This process turns a simple board into a working part of an electronic device.
A PCB is just the bare board with copper pathways.
A PCBA has all the electronic parts attached, making it ready to use.
The main difference is that only PCBA can power devices and make them work.
Key Takeaways
PCBA means a printed circuit board with all electronic parts attached, making it ready to power devices.
PCBA differs from PCB because PCB is just the bare board, while PCBA includes all components and testing.
The assembly process uses two main methods: Surface Mount Technology (SMT) for small parts and Through-Hole Technology (THT) for stronger connections.
Quality control is vital in PCBA to find defects early and ensure devices work reliably and last longer.
PCBA is essential in many fields like consumer electronics, automotive, and medical devices, helping make products smaller, smarter, and more reliable.
What is PCBA
PCBA Meaning
PCBA stands for Printed Circuit Board Assembly. This term describes a printed circuit board after technicians or machines have placed and soldered all the electronic components onto it. The process begins with a bare board, called a PCB. Workers or machines then add parts like resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits. These parts allow the board to perform specific functions inside electronic devices.
A typical PCBA contains many types of components. Some of the most common include:
Resistors
Capacitors
Inductors
Diodes
LEDs
Transistors
Crystals and oscillators
Integrated circuits (ICs)
Relays and switches
Connectors
Sensors
These components work together to control electricity, process signals, and connect to other parts of a device. Each part has a special job. For example, resistors limit current, while capacitors store and release energy.
Note: PCBA uses both surface mount technology (SMT) and through-hole technology (THT) to attach components. SMT places parts directly onto the board’s surface, while THT pushes leads through holes in the board.
PCBA vs PCB
A PCB is just the base board. It has copper tracks and pads but no electronic parts. Manufacturers create PCBs by preparing the base material, drawing circuit patterns, printing conductive layers, etching away extra copper, drilling holes, and sometimes adding a protective coating. This process is important, but the board cannot do anything by itself.
PCBA takes the process further. After making the PCB, workers or machines add and solder all the necessary components. This step makes the board ready to use in a device. The assembly process is more complex than making a bare PCB. It involves:
Sourcing and checking each component
Placing parts with high precision
Soldering using machines or by hand
Testing the finished board to make sure it works
The table below shows the main differences between PCB and PCBA manufacturing:
Aspect | PCB Manufacturing Complexity | PCBA Manufacturing Complexity |
|---|---|---|
Process Steps | Baseboard preparation, graphic drawing, conductive printing, corrosion, drilling, welding | All PCB steps plus component insertion and soldering (SMT, through-hole), component procurement, assembly labor, soldering materials, and testing (ICT, functional) |
Precision Requirements | Moderate, focused on physical board fabrication | High, requires precise and calibrated assembly processes to handle fine-pitch components and high component count |
Time and Cost | Relatively quick and low cost | More time-consuming and costly due to added assembly and testing steps |
Quality Control | Standard fabrication quality checks | Extensive quality control including testing and yield management to ensure functional assemblies |
Design Considerations | Focus on physical layout and manufacturability of the board | Additional focus on design for assembly (DFA) and design for manufacturing (DFM) to optimize component placement and assembly efficiency |
PCBA costs more than a bare PCB. The price of a PCB depends on the number of layers, the size, and the holes needed. PCBA adds the cost of each component, the labor or machines for assembly, and the time for testing. For example, making 30 two-layer PCBA units (80x90mm) costs about $339 in Germany, but only $20 in China. For 1,000 units, the cost per PCBA is about $3.48 in the USA and $0.37 in China. These numbers show that PCBA is more expensive than PCB, and the location of the factory can change the price and speed.
Tip: When planning a project, remember that PCBA includes all the steps and costs of PCB, plus extra work for assembly and testing.
PCBA Assembly Process

The assembly process for a pcba involves several important steps. Each step helps turn a bare board into a working part of an electronic device.
SMT and THT
Two main techniques help attach components to the board: Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Technology (THT).
Feature | Surface Mount Technology (SMT) | Through-Hole Technology (THT) |
|---|---|---|
Component Placement | On the surface using solder paste and reflow oven | Leads go through holes and are soldered on both sides |
Mechanical Bond | Solder holds parts on the surface | Leads pass through the board for a stronger bond |
Assembly Speed | Fast and automated | Slower, often manual |
Cost | Lower due to automation | Higher due to drilling and manual work |
Use Cases | Phones, computers, mass production | Prototyping, connectors, high-stress parts |
Inspection & Repair | Harder due to small size | Easier because leads are visible |
Environmental Tolerance | Less resistant to vibration and heat | More resistant, used in harsh environments |
Most modern devices use SMT for small, lightweight parts. THT works best for parts that need extra strength or must handle stress.
The main steps in the assembly process include:
Solder paste printing on the board pads.
Placing components using pick-and-place machines (SMT) or by hand (THT).
Soldering components with a reflow oven (SMT) or wave soldering (THT).
Inspecting the board for defects.
Washing and drying to remove any leftover flux.
Final testing to make sure the board works.
Quality Control
Quality control ensures every pcba meets strict standards. Manufacturers use several methods to check for problems:
Visual inspection and Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) find missing or misplaced parts.
X-ray inspection checks hidden solder joints.
In-Circuit Testing (ICT) and functional tests verify the board works as designed.
Solderability tests confirm strong, reliable joints.
Adherence to IPC standards, such as IPC-A-610, ensures high quality.
Good quality control helps prevent early failures and keeps electronic devices reliable.
Importance of PCBA
Device Functionality
PCBA forms the heart of every electronic device. By assembling many electronic components onto a single board, it creates a pathway for electricity to flow and signals to travel. Each part, such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits, has a special job. For example, resistors control the amount of current, while integrated circuits process information. When these parts connect on a pcba, the device can perform its intended tasks.
A well-made pcba ensures that all components work together smoothly. Precise soldering and careful placement keep the board strong and reliable. This careful assembly allows devices like smartphones, computers, and medical equipment to function as designed. Without a complete pcba, even the most advanced device would not work.
PCBA also supports miniaturization. Smaller and denser components fit onto compact boards, making devices lighter and more portable. Technologies like surface mount technology and high-density interconnects help engineers design smaller products without losing performance.
Reliability and Performance
Reliability and performance matter in every electronic product. PCBA improves both by using strict quality control and advanced testing. Manufacturers check each board for defects using tools like automated optical inspection and X-ray imaging. These tests catch problems early, such as poor solder joints or misplaced parts.
PCBA reliability increases by preventing common failures like vibration damage, moisture, and dust.
Protective coatings and strong design features help boards survive harsh environments.
Advanced cleaning removes tiny particles that could cause short circuits or failures.
A reliable pcba means fewer breakdowns and longer device life. High-quality assembly also boosts performance by reducing signal loss and interference. This attention to detail ensures that devices run smoothly, even in demanding conditions.
PCBA Applications
Consumer Electronics
PCBA plays a key role in many consumer electronics. People use these devices every day at home, school, and work. The assembly process allows engineers to fit many parts into small spaces, making products lighter and more powerful. Common examples include:
Laptops and desktop computers
Smart home devices such as thermostats, speakers, and security systems
Televisions and gaming consoles
Home appliances like microwaves, refrigerators, and coffee makers
Manufacturers produce these devices in large numbers. They rely on strict quality control to keep each product reliable. The trend of miniaturization pushes designers to create smaller and more complex boards. This helps companies make new products that fit in a pocket or on a wrist.
The market for consumer electronics pcba is very large. The value in 2024 stands at over $25 billion. Smartphones make up about 35% of this market. The Asia Pacific region leads with around 40% of the revenue. The fastest-growing segment is smart wearables, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches.
Metric/Aspect | Value/Description |
|---|---|
Consumer Electronics PCBA Market Size (2024) | Over $25 billion |
Largest Application Segment (2023) | Smartphones (~35% of revenue) |
Asia Pacific Revenue Share (2023) | Approximately 40% |
Fastest Growing Segment |
Automotive and Medical
PCBA also supports important systems in cars and medical devices. In the automotive industry, engineers use pcba to control engine management, infotainment, and safety features. These boards must handle heat, vibration, and shocks. Designers place large parts first and use special materials to improve durability and heat tolerance. Quality and reliability matter because vehicles operate in tough conditions.
Medical devices depend on pcba for accurate and safe operation. Hospitals use these boards in MRI machines, heart monitors, pacemakers, and infusion pumps. The boards must meet strict standards for safety and reliability. Manufacturers use multi-layer designs and careful testing to ensure each board works as needed. Medical pcba production follows rules like ISO 13485 to protect patient health.
The automotive sector expects a 7.2% growth rate, driven by electric vehicles and new technologies. The medical field also shows strong growth as more devices use advanced electronics for diagnosis and treatment.
Sector | Projected Growth Rate (CAGR) | Growth Drivers and Notes |
|---|---|---|
Automotive | 7.2% | Electric vehicles, more electronics per car, battery management, autonomous driving |
Medical | Not stated | Demand for diagnostic equipment, implantable devices, telehealth, and precision assembly |
PCBA helps make modern life safer, smarter, and more connected.
PCBA turns a simple board into the working core of electronic devices. Unlike a bare PCB, it brings together many parts to create smart products for homes, cars, and hospitals. Recent advances include flexible boards, miniaturization, and green materials. As technology grows, PCBA will support new trends like IoT, 5G, and AI. These changes help devices become smaller, faster, and more reliable for the future.
FAQ
What does PCBA stand for?
PCBA stands for Printed Circuit Board Assembly. This term describes a circuit board after workers or machines have attached all the electronic components.
How does PCBA differ from PCB?
A PCB is a bare board with copper tracks. A PCBA has all the electronic parts attached. Only a PCBA can make a device work.
Why is quality control important in PCBA?
Quality control checks each board for problems. It helps prevent failures and keeps devices safe and reliable. Good quality control uses tests like AOI and X-ray inspection.
Which industries use PCBA the most?
Many industries use PCBA. The most common include consumer electronics, automotive, and medical fields. These boards help products like phones, cars, and medical devices work.
Can PCBA be recycled?
Yes, companies can recycle PCBA. They recover metals and some parts. Recycling helps reduce waste and saves resources.
See Also
A Comprehensive Guide To Electronic Digital Integrated Circuits
How ESD Protection Chips Safeguard Electronic Circuitry
The Importance Of MCUs With FPUs In Embedded Systems
Key Differences Between Evaluation And Development Boards Explained
