What Are Intel's AI Solutions and How Do They Work
Intel AI solutions help speed up artificial intelligence tasks from edge devices to the cloud. The company provides a full range of hardware and software, including Xeon processors, Gaudi AI accelerators, and tools like OpenVINO. Intel AI stands out by offering strong price-performance and open networking, which makes AI more cost-effective and flexible for businesses. The company also focuses on responsible AI, aiming for real-world benefits in many industries.
Aspect
Intel AI Stack
Comparison / Context
Price-Performance
Gaudi 3 offers up to 2.3x better price-performance on Llama2-13B; 335% more cost-efficient for large model inference on IBM Cloud
Compared to NVIDIA H100
Open Networking
24x 200Gb Ethernet ports for scalable AI clusters
Reduces vendor lock-in versus proprietary solutions
Key Takeaways
Intel offers a full range of AI hardware and software that work together to speed up AI tasks from edge devices to the cloud.
Xeon processors and Gaudi AI accelerators deliver strong performance and cost efficiency for AI workloads in data centers and at the edge.
OpenVINO and other Intel software tools help developers deploy AI models faster and more efficiently on Intel hardware.
Intel AI supports real-world uses in healthcare, manufacturing, and retail, improving speed, accuracy, and operational efficiency.
Intel follows responsible AI principles to ensure fairness, transparency, privacy, and safety in AI development and deployment.
Overview
What Is Intel AI
Intel AI refers to a set of technologies and solutions that help people and businesses use artificial intelligence in real-world situations. These solutions include hardware, software, and cloud platforms. Intel AI supports everything from training large models in data centers to running quick AI tasks on personal computers and edge devices.
The table below shows how Intel organizes its AI solutions:
Category | Components / Examples | Role and Structure within Intel Ecosystem |
|---|---|---|
AI Hardware | CPUs (5th Gen Xeon Scalable, Core Ultra), GPUs (Data Center GPU Max Series), AI Accelerators (Gaudi2, Gaudi3), AI PCs with integrated NPUs | Provides the foundational compute power for AI training, inference, and deployment across data center, edge, and client devices. |
OpenVINO toolkit, oneAPI, AI libraries, frameworks, reference kits | Enables developers to build, optimize, and deploy AI models efficiently with portability and performance across hardware types. | |
AI Cloud and Developer Environments | Intel Developer Cloud, Intel Tiber AI Cloud | Offers scalable cloud-based environments for AI development, testing, and deployment with access to latest Intel hardware. |
AI Edge and Data Center Compute Solutions | PowerEdge systems with Xeon and Gaudi accelerators, AI PCs with Core Ultra processors | Supports AI workloads from large-scale training in data centers to low-latency inference at the edge and client devices. |
Ecosystem and Partnerships | Open software foundations, developer tools, partnerships | Facilitates AI innovation and deployment through open standards, broad hardware/software integration, and collaborative efforts. |
These categories work together to make AI more accessible, flexible, and powerful for many users.
Key Principles
Intel AI follows important principles to guide its technology and product development:
Compute ubiquity and flexibility help increase performance for many types of AI tasks.
Openness makes it easier for people to use and deploy AI solutions.
Responsibility ensures safe development, data security, and ethical deployment.
Intel also builds its AI solutions on strong values:
Respect human rights for everyone involved.
Enable human oversight so people can control and check AI systems.
Provide transparency and explainability about how AI works and makes decisions.
Advance security, safety, and reliability in every product.
Design for privacy to protect user data.
Promote inclusion and reduce bias in AI systems.
Protect the environment by focusing on energy efficiency and sustainability.
Note: These principles help Intel AI create trustworthy, safe, and effective solutions for people and businesses.
Intel AI Hardware

Xeon Processors
Intel Xeon processors play a central role in powering AI data centers. These CPUs support a wide range of AI workloads, from model training to real-time inference. Intel Xeon 6 processors feature up to 128 performance cores, which helps them handle demanding AI tasks. Priority Core Turbo technology allows the processor to adapt to different AI workload patterns, making it efficient for both sequential and parallel processing.
Intel Xeon processors include advanced AI acceleration technologies. Features like Intel Advanced Matrix Extensions (AMX), AVX-512, and Deep Learning Boost (DL Boost) speed up matrix multiplications and vector computations. These improvements help with deep learning tasks such as image classification and natural language processing. The processors also offer high memory bandwidth, about 30% faster than similar AMD EPYC processors, and provide 20% more PCIe lanes than previous generations. This reduces data transfer bottlenecks in systems that use GPUs for AI.
Intel Xeon 6 processors deliver, on average, 1.4 times better performance than the previous generation across enterprise workloads. They provide up to 1.5 times better AI inference performance than 5th Gen AMD EPYC processors, even when using fewer cores. Performance-per-watt efficiency allows organizations to consolidate servers, reducing total cost of ownership by up to 68%. For example, a 38-core Xeon system can handle int8 inferencing for up to 38 simultaneous camera streams on edge video servers.
Intel Xeon processors hold a leading position as host CPUs for AI servers. However, Intel executives recognize the need to improve their market share in AI data center deployments. They focus on stabilizing and enhancing Xeon's competitive position, especially as AI data centers become a major growth area.
Category | Details |
|---|---|
Market Share of Top 3 Vendors (Intel, AMD, NVIDIA) | |
Intel's Position | Tier 1 vendor alongside AMD and NVIDIA |
Intel Xeon Processors | Key products with AI acceleration and power efficiency |
Specific Intel Xeon Market Share | Not explicitly stated; included within combined 55% share |
Intel's Market Strategy | Focus on stabilizing and improving competitive position in AI data centers in 2025 |
Gaudi AI Accelerators
Intel Gaudi AI accelerators are designed for large-scale AI training and inference. These accelerators help organizations run complex models, such as large language models (LLMs), with high efficiency. Gaudi 2 accelerators reduce latency and time-to-first-token, which improves responsiveness in applications like chatbots. They support high throughput, making them suitable for processing large models such as Llama-3.1B and Falcon-3.10B.
Gaudi 3 builds on the strengths of Gaudi 2. It features 128GB of high-bandwidth memory (HBM), PCIe 5.0 support, and improved power efficiency using TSMC's 5nm process. These upgrades boost AI training performance and energy efficiency. Gaudi accelerators are compatible with popular open-source LLMs, which makes them practical for many enterprises.
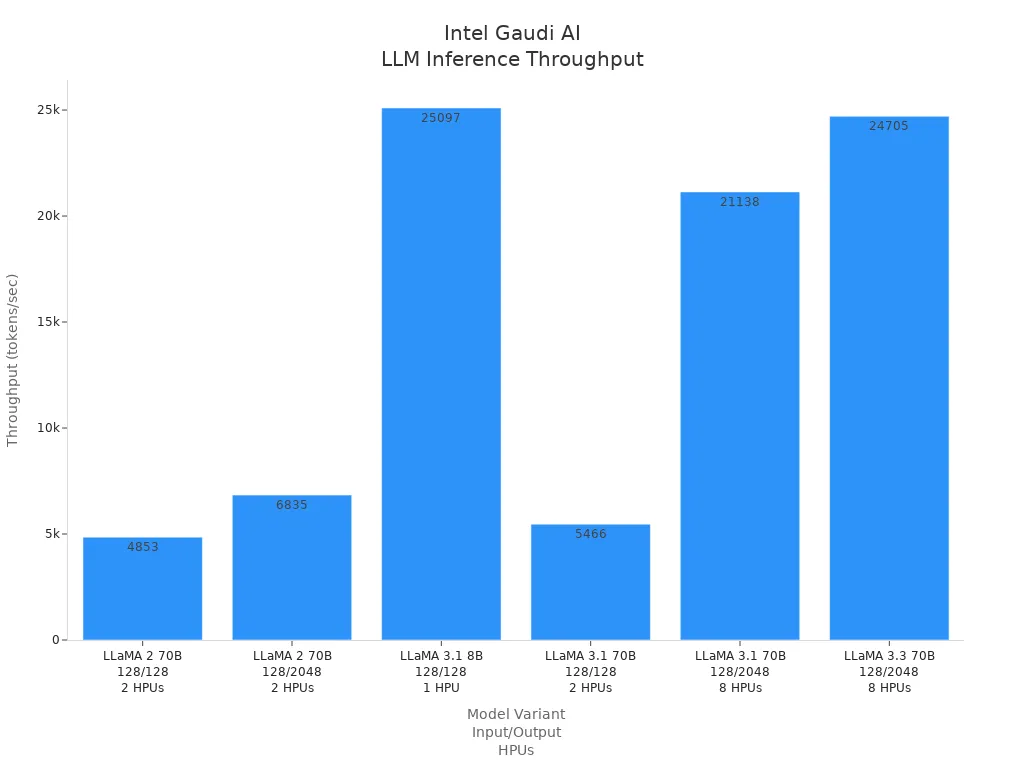
The following table shows benchmark results for Gaudi 3 on different LLaMA model variants:
Model Variant | Precision | Input Length | Output Length | Number of HPUs | Batch Size | Throughput (tokens/sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
LLaMA 2 70B | fp8 | 128 | 128 | 2 | 1750 | ~4,853 |
LLaMA 2 70B | fp8 | 128 | 2048 | 2 | 512 | ~6,835 |
LLaMA 3.1 8B | fp8 | 128 | 128 | 1 | 1536 | ~25,097 |
LLaMA 3.1 70B | fp8 | 128 | 128 | 2 | 2048 | ~5,466 |
LLaMA 3.1 70B | fp8 | 128 | 2048 | 8 | 768 | ~21,138 |
LLaMA 3.3 70B | fp8 | 128 | 2048 | 8 | 2048 | ~24,705 |
Gaudi 3 also stands out for its cost and energy efficiency. The following table compares Gaudi 3 with NVIDIA H100:
Metric | Intel Gaudi3 | NVIDIA H100 | Comparison / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Price per chip | $15,625 | $23,500 - $30,678 | Gaudi3 costs roughly half or less than H100 |
Baseboard (8 accelerators) | $125,000 | $200,000 | Gaudi3 baseboard is significantly cheaper |
Baseboard performance (petaflops, BFP16) | 14.68 | 8 | Gaudi3 offers higher raw petaflops at BFP16 |
Cost per petaflop (baseboard) | $8,515 | $25,000 | Gaudi3 is about 2.9x better price/performance |
Full system cost (incl. CPU, memory, networking, storage) | $275,000 | $375,000 | Gaudi3 system is about 2.5x better price/performance |
Cost per petaflop (full system) | $18,733 | $46,875 | Gaudi3 maintains significant cost efficiency |
TDP (power consumption) | ~600W | Higher (not explicitly stated) | Gaudi3 likely has lower energy consumption |
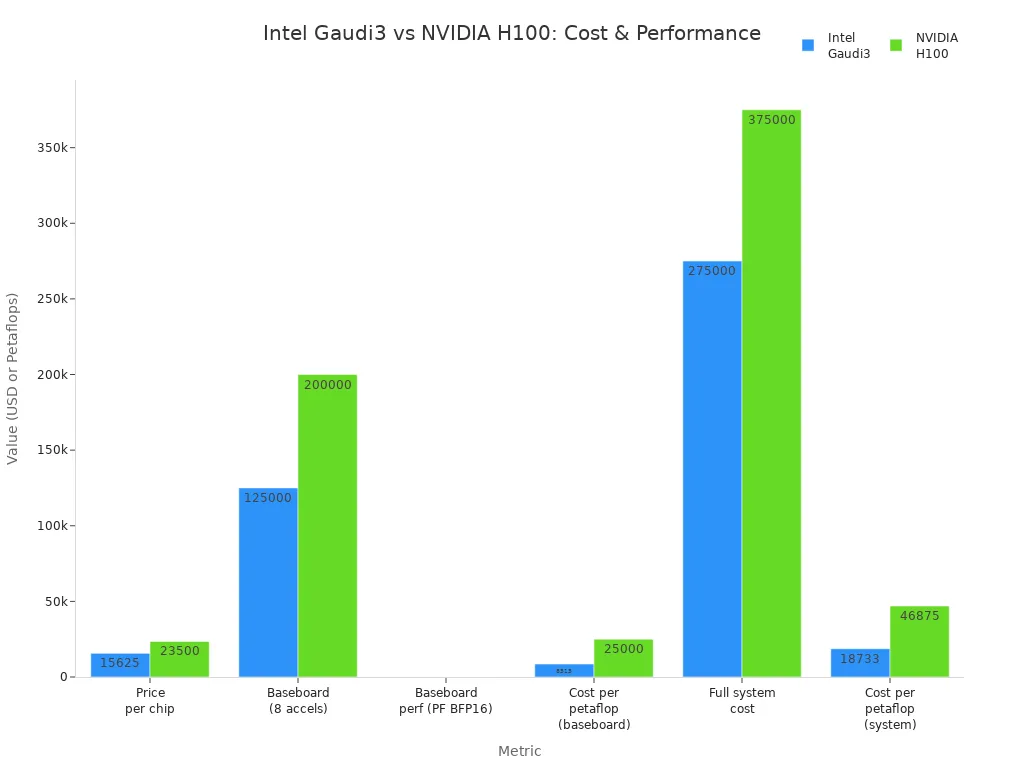
Intel Gaudi3 offers a lower total cost of ownership due to its lower hardware price and reduced energy use. However, NVIDIA has a more mature software ecosystem, which can make deployment easier. Organizations should consider both cost and software support when choosing between Gaudi3 and H100 for AI workloads.
Edge Devices
Edge devices bring AI processing closer to where data is created. This reduces latency and saves bandwidth by processing information locally. Intel supports a wide range of edge AI hardware, including CPUs, GPUs, NPUs, FPGAs, and AI accelerators. These components power solutions in industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, retail, and smart cities.
The table below highlights the types of edge AI hardware and their typical use cases:
Primary Use Cases | |
|---|---|
CPUs, GPUs, NPUs, FPGAs, AI Accelerators | IoT, industrial automation, healthcare, retail, manufacturing, metro, media & entertainment sectors |
Intel AI Edge Systems (partner co-developed, scalable, right-sized) | Real-time video analytics, automated defect detection, asset tracking, smart city applications, live video production, customer checkout automation |
Software frameworks (OpenVINO, Open Edge Platform) | Accelerate AI solution development, deployment, and lifecycle management across industries |
Edge devices powered by intel ai hardware can perform tasks such as real-time video analytics, automated defect detection, and asset tracking. These devices help organizations respond quickly to events and make better decisions at the source of data.
Intel AI Software
OpenVINO
OpenVINO stands for Open Visual Inference and Neural Network Optimization. This toolkit helps developers run AI models faster and more efficiently on Intel hardware. OpenVINO reduces the memory footprint by tracking and managing memory dependencies between operation nodes. This means the toolkit uses improved data structures and logic, which leads to faster inference and better resource use. Developers can choose from multiple precision levels, such as INT4, INT8, FP16, FP32, and BF16. This flexibility helps balance speed and accuracy.
OpenVINO offers a Model Hub with pre-benchmarked performance data. Developers can select hardware platforms, precision levels, and performance metrics like throughput and latency. The toolkit also provides step-by-step tutorials in OpenVINO notebooks, making it easier to deploy and test models on local or cloud hardware.
Many industries use OpenVINO for AI deployment. Enterprises rely on it for large language models and generative AI to improve operations and customer experience. For example, Cisco uses OpenVINO with 5th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable Processors to power chatbots and retrieval-augmented generation pipelines. OpenVINO's Just-In-Time compiler with dynamic shapes support boosts inference performance by 40%. This is especially helpful for transformer-based AI models. In some cases, OpenVINO delivers up to three times faster model inference compared to stock PyTorch models and a 3.5 times improvement in time to first token latency. Intel AMX technology, when used with OpenVINO, can provide up to 10.7 times higher real-time speech recognition inference performance and 7.9 times better performance per watt than previous processors.
Tip: OpenVINO helps companies deploy scalable, cost-effective AI solutions that work in real time, even in environments with limited resources.
Geti Platform
The Intel Geti platform makes AI model development and deployment easier for everyone, including people without deep AI knowledge. Domain experts, such as farmers or factory workers, can help create models without needing to learn coding. The platform supports many computer vision tasks, including object detection, classification, segmentation, and anomaly detection.
Key features of the Geti platform include:
Smart annotation tools that use AI to help label images quickly, reducing manual work.
The ability to start training models with as few as 10-20 images, thanks to active learning and transfer learning.
Support for segmentation tasks, including both instance and semantic segmentation.
Task chaining, which lets users combine multiple models for more complex workflows.
Built-in OpenVINO optimizations for fast and efficient model deployment on Intel CPUs, GPUs, and VPUs.
REST APIs and SDKs for easy integration into production systems.
Flexible deployment options, including local, on-premises, and cloud environments with Kubernetes support.
Intel Geti accelerates training by using transfer learning, which fine-tunes pre-trained models for specific tasks. Active learning helps select the most useful data samples for annotation, making training more efficient. The platform manages the model lifecycle, allowing teams to update and retrain models without downtime. Integration with OpenVINO ensures that models run efficiently on a wide range of Intel hardware. When paired with solutions like Dell NativeEdge, Geti supports scalable and reliable AI deployment at the edge, including features for failure prevention and controlled rollouts.
Note: The Geti platform empowers organizations to build, train, and deploy AI models quickly, even with small datasets and limited technical expertise.
Tiber
Intel Tiber AI Studio serves as a powerful tool for managing AI workflows across hybrid cloud environments. It gives teams visibility into both on-premises GPU clusters and cloud resources, which helps increase GPU utilization and return on investment. Tiber reduces the time researchers spend on engineering and DevOps tasks, making AI development smoother and faster.
Tiber supports hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructures with native Kubernetes orchestration and a meta-scheduler. This setup allows teams to scale machine learning operations, manage resources, and automate workflows from research to production. Tiber works with major cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, unifying data science teams and enabling end-to-end workflow automation.
The Tiber Edge Platform complements AI Studio by managing edge infrastructure. It provides a single view for hybrid edge deployments, supports secure onboarding, and automates AI model deployment and updates across edge nodes. The platform optimizes inference performance and supports closed-loop automation, which improves resilience and efficiency.
Tiber's MLOps Dashboard increases AI pipeline management efficiency. It raises ML infrastructure utilization from about 20% to as high as 70-80%. The dashboard shows real-time resource allocation and usage, helping teams spot bottlenecks and optimize compute power. These improvements reduce wasted resources and improve the return on machine learning projects.
Callout: Tiber helps organizations streamline AI development, deployment, and management across both cloud and edge environments, making it a key part of the intel ai ecosystem.
AI Workflows

Edge to Cloud
Intel AI solutions support seamless deployment from edge devices to the cloud. Many organizations use Intel’s open, modular edge platform to process data close to its source. This approach reduces latency and network bottlenecks, which is critical for real-time applications. Edge AI systems, such as those in retail or manufacturing, often operate in space-constrained and low-power environments. Intel’s platform integrates OpenVINO for optimized AI inference, enabling fast and cost-effective deployments. Companies can manage AI workloads across different devices and cloud environments using a single dashboard. Features like zero-touch provisioning and secure remote management simplify operations. Intel’s ecosystem of partners helps deliver industry-specific solutions, such as smart city traffic control and industrial defect detection.
Tip: Processing data at the edge with Intel AI improves operational speed and efficiency while lowering costs.
Real-World Use Cases
Intel AI drives innovation in several industries:
Healthcare: Hospitals use AI to analyze medical images like X-rays and ultrasounds. Processing data locally helps protect patient privacy and speeds up diagnosis. AI also automates clinical documentation, reducing burnout for doctors and nurses.
Manufacturing: Factories use AI to scan parts for defects faster than human inspectors. This improves quality control, increases throughput, and enhances worker safety.
Retail: Stores use AI for shelf monitoring and inventory management. AI tracks stock levels and customer behavior, helping retailers reduce losses and improve shopping experiences.
Organizations report measurable results, such as a 50% reduction in time spent on routine tasks and faster decision-making after adopting Intel AI solutions.
Getting Started
Organizations can follow these steps to begin their AI journey:
Check if existing infrastructure supports AI workloads.
Identify gaps in skills or tools and plan to address them.
Start with small AI projects to test and learn.
Use best practices and case studies to guide adoption.
Intel offers many resources to help new users, including:
Resource Type | Examples |
|---|---|
Development Tools | |
Pretrained Models | OpenVINO models, Gaudi AI Accelerator Models |
Training Platforms | Intel Tiber AI Cloud, OpenVINO DevCon |
Community Support | Developer forums, workshops, expert help |
Note: Intel’s developer forums, quick start guides, and partner collaborations make it easier for teams to build and deploy AI solutions.
Responsible AI
Fairness and Efficacy
Intel’s responsible AI framework stands on four main pillars:
Internal and External Governance: Multidisciplinary advisory councils review AI development. These councils check for respect for human rights, privacy, equity, and environmental protection. Intel also takes action if products are misused, including ending business relationships when human rights are at risk.
Research and Collaboration: Intel works with universities and industry groups worldwide. These partnerships focus on privacy, security, explainability, and sustainability. Centers of excellence help guide ethical and user-focused AI development.
Products and Solutions: Intel creates platforms and tools that make responsible AI possible. These tools improve privacy, security, transparency, and reduce bias. Ethnographic research helps address real-world problems.
Inclusive AI: Diversity, equity, and inclusion are key. Intel supports outreach programs and works with many educational groups to make AI more accessible.
To ensure fairness and efficacy, Intel uses several steps:
Governance structures enforce fairness, transparency, and accountability.
Collaboration spaces bring together developers, managers, and community members. This helps everyone share ideas and power.
Technical reviews check data and test for fairness before and after deployment. Results are shared with people outside the development team.
Training programs teach developers about transparency and explainability. Soft skills training helps reduce bias.
Intel’s Responsible AI Program encourages teamwork with industry and academia. Intel Labs works to reduce bias by using trusted sources and diverse data. Open-source datasets help improve fairness for everyone.
Fairness and efficacy in AI mean that systems work well for all people and do not create or reinforce bias.
Transparency and Accountability
Transparency and accountability are central to Intel’s approach. Since 2017, Intel has run a Responsible AI program based on principles like transparency, explainability, human oversight, and privacy by design. Advisory councils and ethics audits review AI projects. Intel also works with universities and groups like MLCommons and the AI Alliance to set standards and benchmarks.
Intel builds explainable AI models and addresses ethical issues in research and deployment. Ethics education is part of workforce training, covering applied ethics and environmental sustainability. Intel also reviews projects at events like the AI Global Impact Festival to ensure ethical standards.
Intel’s efforts extend to the supply chain, improving human rights for workers involved in AI data tasks. The company continues to address risks from new AI technologies, focusing on safety, security, and trust.
These actions help build trust in AI systems and ensure they are used responsibly.
Intel’s AI solutions deliver flexibility and efficiency for many industries. Key benefits include:
Xeon processors and Gaudi accelerators support AI workloads in data centers and at the edge.
Software tools like OpenVINO help developers deploy models faster.
Real-world success stories show improved speed and accuracy in healthcare, retail, and manufacturing.
Partnerships with companies such as Cisco and CDW provide expert support and ready-to-use solutions.
Area | Impact Example |
|---|---|
Healthcare | Faster X-ray analysis with OpenVINO |
Manufacturing | Automated defect detection at the edge |
Retail | Enhanced customer experience and operations |
Intel’s focus on responsible AI and ecosystem collaboration helps organizations adopt AI with confidence.
FAQ
What makes Intel AI hardware different from others?
Intel AI hardware offers strong price-performance and open networking. Xeon processors and Gaudi accelerators support many AI tasks. These devices help businesses save money and avoid vendor lock-in.
Can someone use Intel AI solutions without deep technical skills?
Yes. Platforms like Intel Geti allow people without coding experience to build and deploy AI models. The tools use smart features and guides to help users at every step.
How does Intel help keep AI fair and safe?
Intel uses a responsible AI framework. This includes fairness checks, transparency, and human oversight. Advisory councils and training programs help teams build ethical and safe AI systems.
Which industries benefit most from Intel AI?
Healthcare, manufacturing, and retail see big gains. Hospitals use AI for faster scans. Factories improve quality control. Stores track inventory and customer needs with AI.
Where can developers find resources to start with Intel AI?
Developers can visit Intel’s website for toolkits, pretrained models, and guides. Community forums and workshops also offer support and learning materials.
See Also
Understanding IC Voice Processors And Their Functionality
Exploring IC Audio Signal Processors And Their Main Features
How Industrial Control Chips Operate Within Automation Systems
The Role And Operation Of Fully Integrated Processors Explained
